자바스크립트에서 객체지향 프로그래밍이란?
자바스크립트 객체지향 프로그래밍
프로토타입 기반 언어
자바스크립트는 명령형, 함수형, 프로토타입 기반 객체지향 언어입니다. 간혹 클래스가 없어서 객체지향이 아니라고 생각하는 사람들도 있으나 프로토타입 기반의 객체지향 언어입니다.
자바스크립트에는 클래스 개념이 없고 별도의 객체 생성 방법이 존재합니다.
- 객체 리터럴
- Object() 생성자 함수
- 생성자 함수
// 객체 리터럴
var obj1 = {};
obj1.name = 'Lee';
// Object() 생성자 함수
var obj2 = new Object();
obj2.name = 'Lee';
// 생성자 함수
function F() {}
var obj3 = new F();
obj3.name = 'Lee';자바스크립트는 다른 언어와는 다르게 이미 생성된 인스턴스의 자료구조와 기능을 동적으로 변경시킬 수 있습니다. 또 상속, 캡슐화 등의 객체지향의 개념을 프로토타입 체인과 클로저 등으로 구현할 수 있습니다.
클래스 기반 언어에 익숙한 프로그래머들(마치 자바를 하던 나..)은 이러한 프로토타입 기반의 특성으로 혼란을 느낄 수 있습니다.
ECMAScript 6에서 새롭게 클래스가 도입되었다. ES6의 Class는 기존 prototype 기반 객체지향 프로그래밍보다 Class 기반 언어에 익숙한 프로그래머가 보다 빠르게 학습할 수 있는 단순하고 깨끗한 새로운 문법을 제시하고 있다. ES6의 Class가 새로운 객체지향 모델을 제공하는 것이 아니며 Class도 사실 함수이고 기존 prototype 기반 패턴의 Syntactic sugar이다.
생성자 함수와 인스턴스의 생성
자바스크립트에서는 생성자 함수(객체를 생성하는 함수)와 new 연산자를 통해 인스턴스를 생성할 수 있습니다. 이때 생성자 함수는 클래스이자 생성자의 역할을 합니다.
// 생성자 함수(Constructor)
function Person(name) {
// 프로퍼티
this.name = name;
// 메소드
this.setName = function (name) {
this.name = name;
};
// 메소드
this.getName = function () {
return this.name;
};
}
// 인스턴스의 생성
var me = new Person('Lee');
console.log(me.getName()); // Lee
// 메소드 호출
me.setName('Kim');
console.log(me.getName()); // Kim위 코드는 잘 동작하지만 만약 Person 생성자 함수로 여러개의 인스턴스를 생성하면 setName, getName이라는 메소드가 중복되어 생성됩니다. 이는 메모리 낭비인데 인스턴스가 많아지거나 메소드가 크거나 많다면 문제가 커질 수 있습니다.
이러한 문제를 프로토타입의 특징을 사용해 해결할 수 있습니다.
프로토타입 체인과 메소드
모든 객체는 프로토타입이라는 다른 객체를 가리키는 내부 링크를 가지고 있습니다. 프로토타입을 통해 직접 객체를 연결할 수 있는데 이를 프로토타입 체인이라고 합니다.
프로토타입을 이용하여 생성자 함수 내부의 메소드를 생성자 함수의 prototype 프로퍼티가 가리키는 프로토타입 객체로 이동시키면 생성자 함수에 의해 생성된 모든 인스턴스는 프로토타입 체인을 통해 프로토타입 객체의 메소드를 참조할 수 있습니다.
function Person(name) {
this.name = name;
}
// 프로토타입 객체에 메소드 정의
Person.prototype.setName = function (name) {
this.name = name;
};
// 프로토타입 객체에 메소드 정의
Person.prototype.getName = function () {
return this.name;
};
var me = new Person('Lee');
var you = new Person('Kim');
var him = new Person('choi');
console.log(Person.prototype);
// Person { setName: [Function], getName: [Function] }
console.log(me); // Person { name: 'Lee' }
console.log(you); // Person { name: 'Kim' }
console.log(him); // Person { name: 'choi' }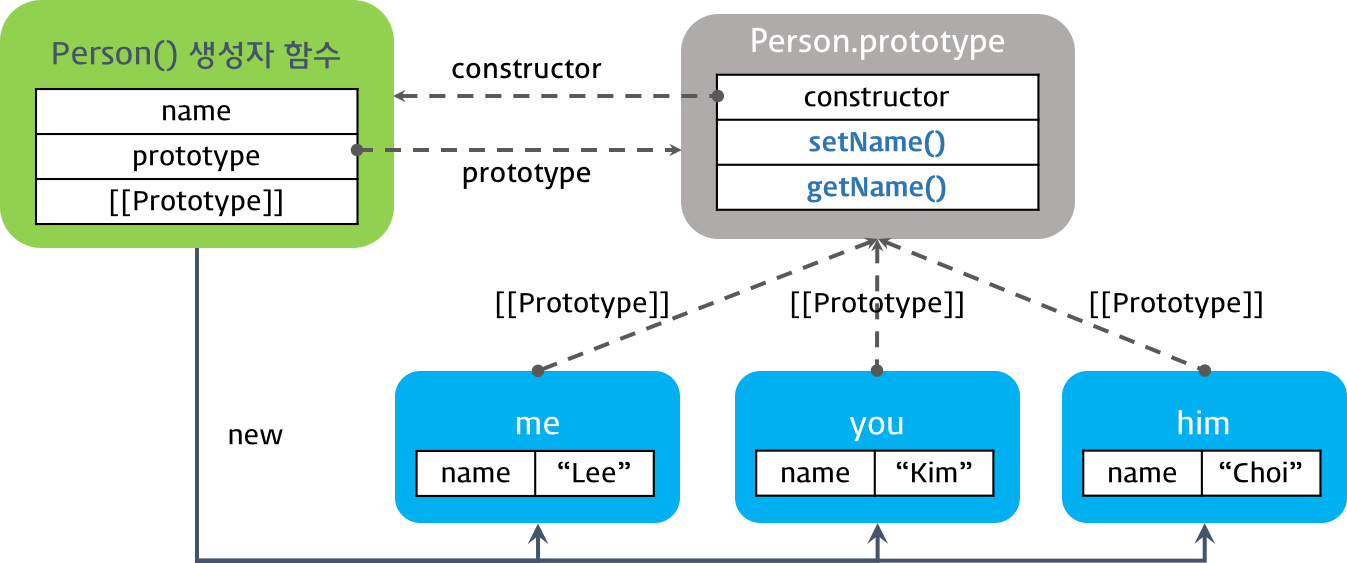
아래는 더글라스 크락포드가 제안한 프로토타입 객체에 메소드를 추가하는 방식입니다.
/**
* 모든 생성자 함수의 프로토타입은 Function.prototype이다. 따라서 모든 생성자 함수는 Function.prototype.method()에 접근할 수 있다.
* @method Function.prototype.method
* @param ({string}) (name) - (메소드 이름)
* @param ({function}) (func) - (추가할 메소드 본체)
*/
Function.prototype.method = function (name, func) {
// 생성자함수의 프로토타입에 동일한 이름의 메소드가 없으면 생성자함수의 프로토타입에 메소드를 추가
// this: 생성자함수
if (!this.prototype[name]) {
this.prototype[name] = func;
}
};
/**
* 생성자 함수
*/
function Person(name) {
this.name = name;
}
/**
* 생성자함수 Person의 프로토타입에 메소드 setName을 추가
*/
Person.method('setName', function (name) {
this.name = name;
});
/**
* 생성자함수 Person의 프로토타입에 메소드 getName을 추가
*/
Person.method('getName', function () {
return this.name;
});
var me = new Person('Lee');
var you = new Person('Kim');
var him = new Person('choi');
console.log(Person.prototype);
// Person { setName: [Function], getName: [Function] }
console.log(me); // Person { name: 'Lee' }
console.log(you); // Person { name: 'Kim' }
console.log(him); // Person { name: 'choi' }상속
자바스크립트는 상속이란 개념을 프로토타입을 통해 구현하는데 이것은 프로토타입을 통해 객체가 다른 객체로 직접 상속된다는 의미입니다.
상속 구현 방식은 크게 두 가지로 구분할 수 있습니다. 하나는 클래스 기반 언어의 상속 방식을 흉내내는 의사 클래스 패턴 상속이고 두번째는 프로토타입으로 상속을 구현하는 프로토타입 패턴 상속입니다.
의사 클래스 패턴 상속
의사 클래스 패턴은 자식 생성자 함수의 prototype 프로퍼티를 부모 생성자 함수의 인스턴스로 교체하여 상속을 구현하는 방법입니다. 부모와 자식 모두 생성자 함수를 정의해야 합니다.
// 부모 생성자 함수
var Parent = (function () {
// Constructor
function Parent(name) {
this.name = name;
}
// method
Parent.prototype.sayHi = function () {
console.log('Hi! ' + this.name);
};
// return constructor
return Parent;
}());
// 자식 생성자 함수
var Child = (function () {
// Constructor
function Child(name) {
this.name = name;
}
// 자식 생성자 함수의 프로토타입 객체를 부모 생성자 함수의 인스턴스로 교체.
Child.prototype = new Parent(); // ②
// 메소드 오버라이드
Child.prototype.sayHi = function () {
console.log('안녕하세요! ' + this.name);
};
// sayBye 메소드는 Parent 생성자함수의 인스턴스에 위치된다
Child.prototype.sayBye = function () {
console.log('안녕히가세요! ' + this.name);
};
// return constructor
return Child;
}());
var child = new Child('child'); // ①
console.log(child); // Parent { name: 'child' }
console.log(Child.prototype); // Parent { name: undefined, sayHi: [Function], sayBye: [Function] }
child.sayHi(); // 안녕하세요! child
child.sayBye(); // 안녕히가세요! child
console.log(child instanceof Parent); // true
console.log(child instanceof Child); // true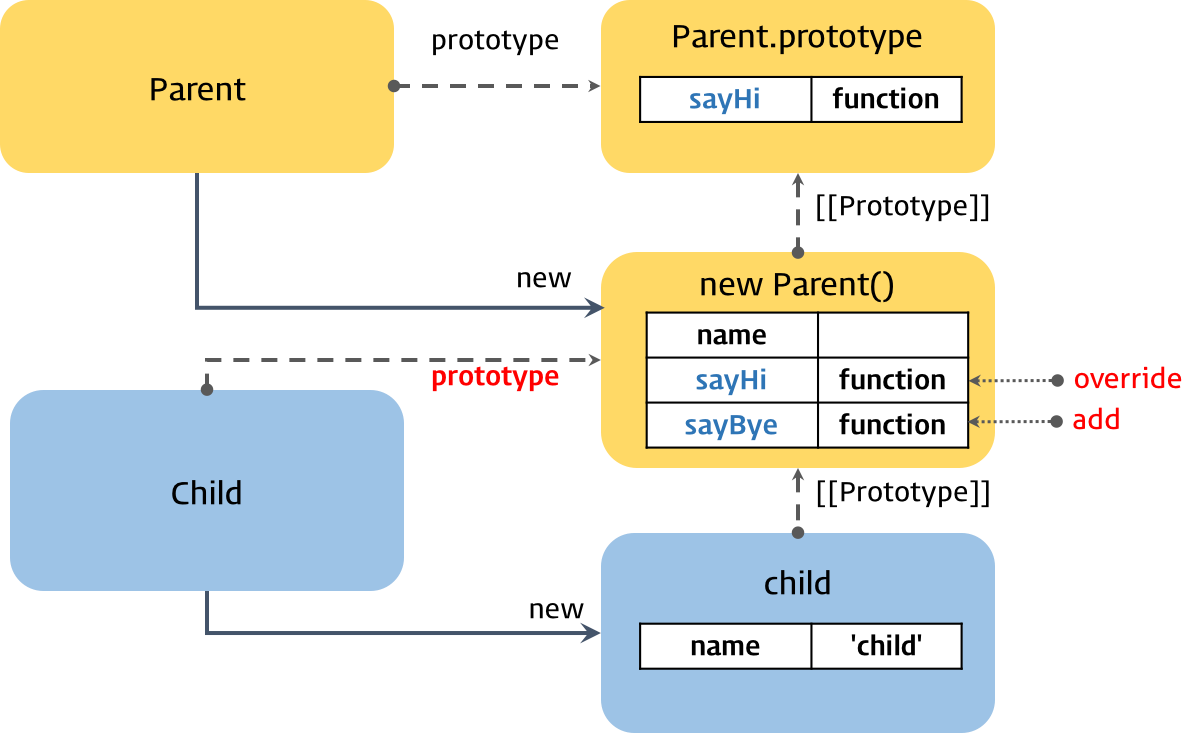
구동 상에 문제는 없지만 아래와 같은 문제를 가지고 있습니다.
- new 연산자를 통해 인스턴스를 생성합니다.
- 생성자 링크의 파괴
의사 클래스 패턴 상속은 프로토타입 객체를 인스턴스로 교체하는 과정에서 constructor의 연결이 깨지게 됩니다.
- 객체리터럴
의사 클래스 패턴 상속은 기본적으로 생성자 함수를 사용하기 때문에 객체리터럴 패턴으로 생성한 객체의 상속에는 적합하지 않다.
프로토타입 패턴 상속
프로토타입 패턴 상속은 Object.create 함수를 사용하여 객체에서 다른 객체로 직접 상속을 구현하는 방식이다. 프로토타입 패턴 상속은 개념적으로 의사 클래스 패턴 상속보다 더 간단하다. 또한 의사 클래스 패턴의 단점인 new 연산자가 필요없으며, 생성자 링크도 파괴되지 않으며, 객체리터럴에도 사용할 수 있다.
// 부모 생성자 함수
var Parent = (function () {
// Constructor
function Parent(name) {
this.name = name;
}
// method
Parent.prototype.sayHi = function () {
console.log('Hi! ' + this.name);
};
// return constructor
return Parent;
}());
// create 함수의 인수는 프로토타입이다.
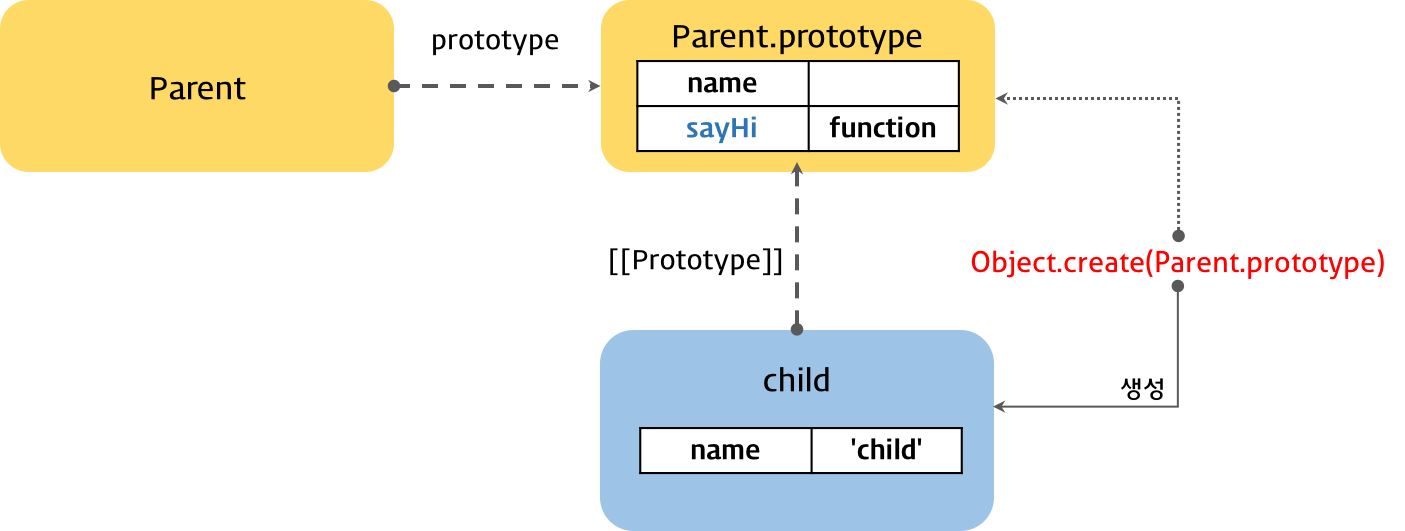
var child = Object.create(Parent.prototype);
child.name = 'child';
child.sayHi(); // Hi! child
console.log(child instanceof Parent); // true